Gas Plug Valve
Gas Plug Valve
Size: 1/2″-6″
Class: 150LB~300LB
End: Flange / BW / NPT
Material: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, CI, Alloy Steel
Seal: Dynamic stem seal design, soft seal, easy to escape medium with bellows seal
What is a gas plug valve?
Gas plug valves are flow control valves used to regulate flow of gases such as natural gas, oxygen, and liquefied petroleum among others. These valves are either lubricated or non-lubricated. The non-lubricated valves are economical since they rarely need repair and maintenance. Gas plug valves are operated manually or automatically. The operation of this valve whether it is manual or automatic is the same. The valve plug rotates for a quarter turn to either start or stop gas flow. Gas plug valve manufacturers design these valves using different materials such as metallic alloys, rubber, and plastic. The choice of material used to make the valve or certain component of the valve will determine among other factors, the area of applications.
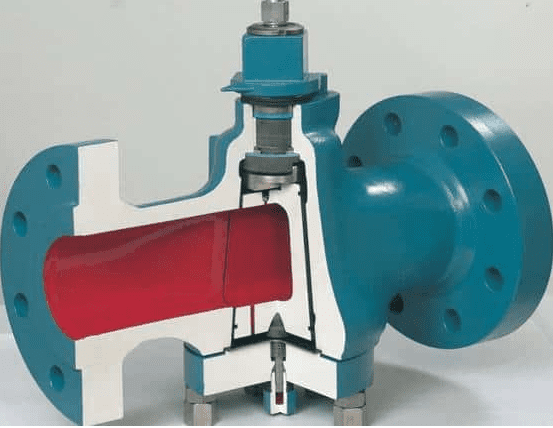
Construction of gas plug valves
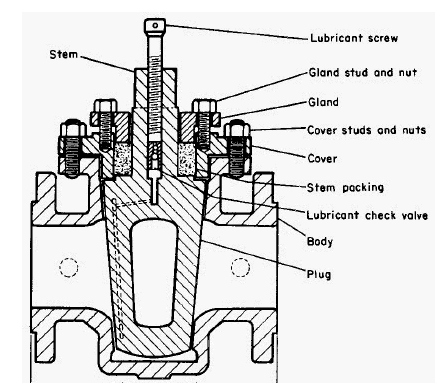
The basic construction of a gas plug valve consists of valve body, body cover, stem, gland packing, gasket, plug, handle, and connecting elements. The valve body is the component that houses internal parts of the valve such as the seat, plug, and seals. Gas plug valve manufacturers design the body to have high strength that ensures the valve can operate at high pressure and high temperature as well as make it secure against impact damage. The body cover is placed on top of the valve body. The cover and the valve body are connected using bolts and nuts or screw threads. The body cover provides the opening for cleaning or repairs when necessary. The cover also helps to house internal parts like gland packing and seals.
The handle is used by the valve operator to apply torque to operate the valve. The handle is connected to the valve plug via the stem. The stem is connected to the handle and it serves to transmit torque from the handle to the plug. Gas plug valve manufacturers make the stem from strong metallic materials to ensure it is strong enough to rotate the valve plug. The valve plug is used to close or open the valve. Gasket is placed between the valve body and pipe to enhance a bubble-tight seal against fluid leakage. The gasket is also placed between the body and top cover to ensure zero leakage. Connecting elements include bolts and nuts used to connect the valve to the pipe or the valve body to the body cover.
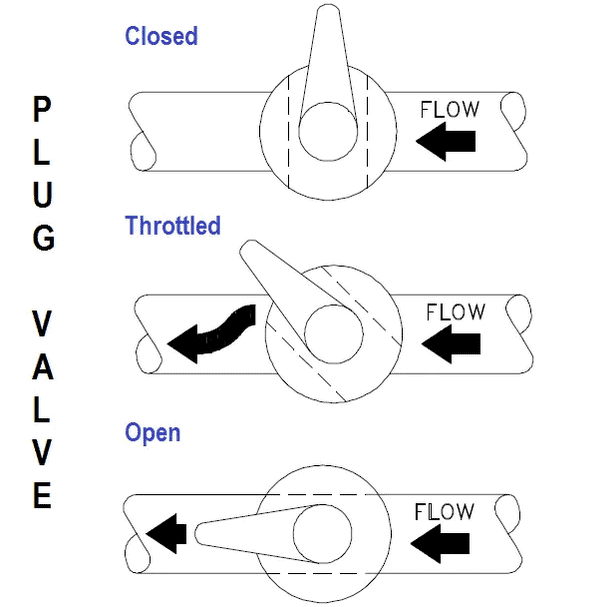
How does a gas plug valve work?
The operation of a gas plug valve is based on the rotation of the valve handle. By rotating the handle, the valve stem also rotates and the same occurs on the valve plug. Gas plug valve manufacturers use a quarter turn concept to make this valve open by just rotating the plug for 90o degrees. To start gas flow through this valve, the handle is rotated in the clockwise direction for a quarter turn. As such, the stem and thus the valve plug makes the same rotation. This rotation helps to align the plug port collinear to the valve port. By making such alignment, the fluid finds the valve free to flow through. To stop gas flow, the handle is rotated again but in the opposite direction which is counterclockwise. This rotation aligns the plug port perpendicular to the gas plug valve port hence blocking fluid flow. For throttling flow, the valve plug is rotated slightly by an angle of less than 90o degrees depending on the flow rate needed.
Types of gas plug valves
Threaded end gas plug valves
This is the gas plug valve with threaded ends on the inlet and exit ports. This valve is easy to install and offers a tight seal if used at the recommended fluid pressure. Gas plug valve manufacturers machine the threads to either be male or female. For the male threaded valve, the pipe end is machined with female threads and vice versa. This valve is suitable for use in gaseous applications where there are no slurries or viscous fluids to cause blockage. Also, this type of valve is small in size which makes it suitable for use where space is limited.
Figure: Threaded end gas plug valves.
Flanged end gas plug valves
This is the type of gas plug valve suitable for use in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Gas plug valve manufacturers make this type of valve from strong metallic materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and ductile iron among others. Such materials make the valve strong enough to operate without failing due to high pressure or high temperature. This valve is connected to the pipeline using bolts and nuts. As the name suggests, this valve has flanged ends on the inlet and outlet ports. The flanged ends have holes of equal size and number and are used to hold the bolts that connected the valve and the pipe.
Gas plug valve manufacturers produce this valve for use in high-pressure applications since with the high torque provided by the several bolts and nuts the fluid cannot leak. However, this valve is usually large and is thus suitable for use where space is not limited. Also, the valve is heavy and the piping system should as well be strong to withstand the weight.
Figure: Flanged end gas plug valve.
Multi-port gas plug valve
This is a special gas plug valve that has three or four ports. Gas plug valve manufacturers design this valve for use in applications that involve fluid diversion and or mixing. This ensures that gas from different pipes can be mixed in one valve and then allowed to leave as one fluid stream. For diversion, the fluid flow direction is changed to an angle of 90o degrees. This type of valve does the work that can be done using three or four gates which helps to reduce the cost of the piping system.
Figure: Multi-port gas plug valve.
Actuated gas plug valves
This is the gas plug valve which is operated automatically. Gas plug valve manufacturers recommend valve in applications that involve a lot of operating torque and where frequent valve operation is desired. This type of valve helps to reduce fatigue to the valve operator. However, this type of valve is quite expensive compared to those operated manually. The additional cost arises from the cost of the actuator as well as the automated system that coordinates the operation of the valve. Actuated gas plug valve manufacturers design three types of actuators that are pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic actuators that can be used to operate this valve.
The electric actuator uses electrical energy (electricity) to operate. It has a system that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy in terms of torque. A pneumatic actuator uses compressed gas to operate. The compressed gas acts on a piston to produce the torque that operates the valve plug to open or close. This type of valve is very reliable for use even in applications involving high temperatures and high pressure. The hydraulic actuator uses hydraulic fluids. This actuator is able to produce a lot of torque because hydraulic fluids are not compressible. However, use of this valve is restricted to applications where high temperatures are not involved.
Figure: Actuated gas plug valve.
PTFE-lined gas plug valves
This is a gas plug valve meant for use in industries that handle corrosive gases such as ammonia, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and hydrogen chloride among others. Gas plug valve manufacturers use PTFE material to cover the interior of the valve. The PTFE material is a thermoplastic material that is highly resistant to corrosion and of a high melting point of around 250 oC. Due to these properties, gas plug valve manufacturers use it to handle fluids at high temperatures as well as prevent the fluid from corroding internal parts of the valve. This type of valve is not lubricated but it uses a sleeve between the plug and the valve body to enhance smooth operation. The sleeve is also made of the same PTFE material. This material has slippery properties which enhances the smooth rotation of the valve plug without wear.
Figure: PTFE-lined gas plug valve.
Applications of gas plug valves
- Gas plug valves are used in the transportation of natural gas.
- It is used in medical applications to control flow of oxygen gas.
- This type of valve is used in steam power plants to control flow of steam and water used to run steam turbines.
- Gas plug valves are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems (HVAC).
- This type of plug valve is used in the manufacturing of gases such as nitrogen, ammonia and oxygen.
- Gas plug valves are used in the processing of hydrocarbons.
Advantages of gas plug valves
- Gas plug valves operate very fast unlike other valves like gate valves.
- These valves can be operated by use of the handle or using actuators.
- Gas plug valves are free from leakage if used at the recommended fluid pressure.
- The pressure drop in these valves is very low compared to other valves like globe and or gate valves.
- These valves can be used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
- Gas plug valves are versatile as they are used in many industrial applications.
- They are resistant to corrosion.
- These valves are of simple and compact construction.
- They are easy to install, repair, and clean.
Disadvantages of gas plug valves
- Gas plug valves are of high weight due to the strong metallic components used to make them.
- These valves need actuators where the valve needs a lot of torque to operate or it needs operation frequently.
- Gas plug valves have a lot of pressure drop when used as throttling valves.
Troubleshooting gas plug valves
No gas flowing through the valve
- Pipe obstruction. Check the pipe for obstruction and remove any material blocking fluid flow.
- Foreign materials in the valve. Open the valve and clean off blocking materials.
The handle is hard to operate
- Dirt between the stem and the body cover. Open the valve according to the procedure given by the gas plug valve manufacturer and remove the dirt.
- The stem is damaged. Replace the stem.
- High fluid pressure. Reduce the fluid pressure.
The actuator does not operate
- No power supply. Check the actuator main supply is connected.
- Low voltage. Ensure the valve voltage value is the one recommended by the gas plug valve operator.
Fluid leakage through the body and pipe joint
- Loose connection. Tighten the connecting bolts to attain the torque mentioned by the gas plug valve manufacturer.
- Worn out or damaged gasket. Replace the gasket.
- Excess gas pressure. Reduce the gas pressure.
Leakage through the stem
- Worn out or damaged packing. Replace the gland packing.
- Worn out seals. Replace the seals.
Summary
Gas plug valves are valves used to handle gaseous products in different industrial applications. These valves are made of different materials and are of different sizes. Gas plug valve manufacturers design this valve to operate by turning the handle or by using an actuator. The handle/actuator rotates forcing the valve plug to make a quarter turn. This quarter turn of the plug aligns the plug port with the valve port allowing fluid flow through the valve. Another opposite quarter turn of the plug closes the valve. This type of valve can be lubricated or non-lubricated. The non-lubricated gas plug valve use a sleeve between the plug and the valve body to enhance smooth operation preventing any wear of the plug. The non-lubricated type has few maintenance requirements unlike the lubricated type.
Various types of valves made by gas plug valve manufacturers include threaded end gas plug valves, flanged end gas plug valves, PTFE-lined gas plug valves, multi-port gas plug valves, and actuated gas plug valves among others. The applications of gas plug valves include manufacturing of gases, hospitals, steam power plants, HVAC systems, and transportation of natural gas among others. Advantages of having a gas plug valve are fast operation, corrosion resistance, versatility, easy installation and repair, low-pressure drop, and high strength.