Lubricated Plug Valve
Lubricated Plug Valve
※ Oil-Lubricated, Pressure Balance
※ Size Range: NPS 2 to NPS 32
※ Pressure Range: 150LB to 2500LB
※ Design STD.: API599/ API6D
※ Lubricated Plug Valve Manufacturer & Supplier
Valves are critical components of a pipe system that transfers liquids, gases, vapors, slurries, and other substances from one location to another. When the media to be transferred contains slightly abrasive particles, mostly a Lubricated Plug Valve is used. It is a quarter-turn valve, which is beneficial for rapid and frequent operation.
Generally, a plug valve has a cylinder or cone type shape that is rotated inside the valve housing to control fluid flow. In addition, the plug valves are frequently positioned horizontally in one or more hollow passages that facilitate the flow of the valve while it is open. The 2-port design with a closed and open state is the most common design of the plug valve.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the plug valve, let’s find out in detail what is a lubricated plug valve, how does it work, its unique features, benefits, and applications.
What Is A Lubricated Plug Valve?
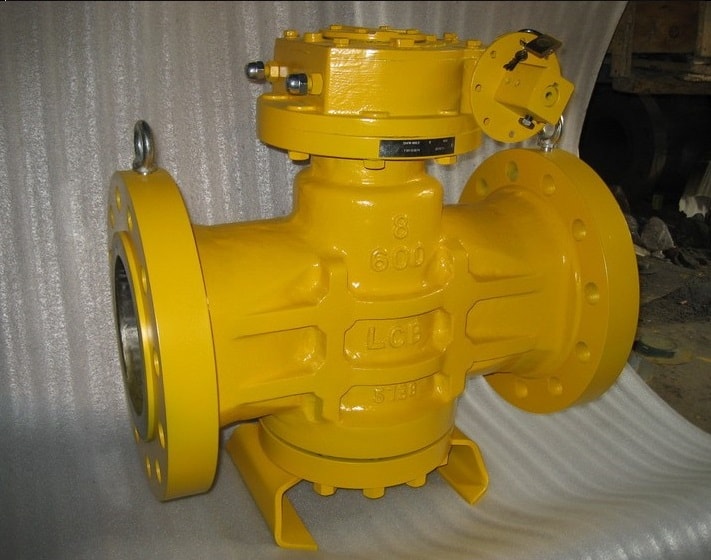

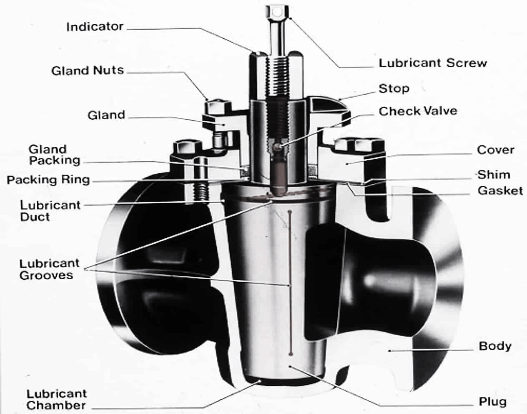
A lubricated plug valve is, as its name, used to decrease friction and sealing of the ports by using the lubricant generally consists of a base oil and viscosity improver that is injected under pressure between the face and the body seat in the plug.
In general, valve manufacturers suggest lubricants that are suited to the fluid process, and valves frequently have to reseal after just a few cycles and in certain circumstances after every cycle.
The tightly sealed seat with lubricating oil is meant to decrease friction between the valve body and the sealing surface of the plug. A layer of oil film between the valve body and the sealing surface of the plug cone confirms the tight seal and smoothens the open/close motion when high-pressure sealing oil is injected around the plug to form a high-pressure seal ring.
How Does A Lubricated Plug Valve Work?
A lubricated plug valve constitutes a cavity in the center of the plug that runs down its axis. This cavity is blocked at the bottom and has a sealant-injection fitting at the top. The sealant is poured into the cavity, and a check valve located underneath the injection fitting stops the sealant from flowing backward. The sealant flows out of the center cavity through radial openings into lubricating grooves that run the length of the plug’s seating surface.
The lubricant substance must be compatible with the pipeline fluid. It should not degrade or be washed away by the flow medium since this might pollute the fluid and break the seal between the plug and the body, leading to leakage. Furthermore, the sealant employed must be able to resist the flow medium’s temperature.
Lubricants Used In A Plug Valve
The term lubricant does not accurately describe the role of this substance in the effective operation of lubricated plug valves. Such valves should be named plastic sealed valves, and the lubricant should be called a plastic sealant. The use of an effective lubricant is critical since the valve structure and a plastic scaling film are integrated units in operation, and each component is dependent on the other for a final performance.
As it offers a flexible and renewable seat, the lubricant effectively becomes a structural component of the valve. This removes the need for force fits and distortable-seat contacts to form a seal. However, to avoid the damaging effect of the line fluid and establish an unbreakable seal around each body port, the lubricant must demonstrate adequate flexibility and resistance to solvents and chemicals.
The lubrication layer also prevents corrosion on the metal surfaces between the plug and the body. The seal produced by the lubricant injected through a system of lubrication grooves circuiting each port assists in the maintenance of the necessary film on the metal, closing surfaces.
Features And Benefits Of Lubricated Plug Valve
The all-metal structure is common in plug valves. The little gap surrounding the plug may enable leakage, and if the gap is further reduced, friction will occur, and the plug may become trapped inside the valve body. The lubricant also decreases the amount of effort needed to open or shut the valve, allowing the plug to move smoothly. It also protects the plug from corrosion.
Sealant supports in the formation of a renewing the seal between the plug and the body, preventing internal leaking. It also keeps the sitting surface from corroding. It also works as a lubricant, reducing the amount of force necessary to operate the valve. Lubricant pressure lifts the plug up from the seat for a brief period, making it easier to spin. Furthermore, the high pressure ensures that no sediments are trapped between the valve body and the plug.
Lubricants used in a plug valve are, in fact, plastic sealants. Therefore, it is critical to use an efficient sealant with qualities such as appropriate elasticity, tolerance from solvents and chemicals, and the capacity to establish an impermeable seal around each body component even when it’s under pressure. The lubrication layer also prevents corrosion on the metal surfaces between the plug and the body.
Lubricated plug valves are produced in a wide variety of sizes and are suitable for use in high-pressure & temperature services. They are available in different sizes ranging from half an inch to 24 inches in length and with pressure capacities of up to 6000 psi. They are available with steel or iron bodies. In some operating conditions, these valves are less prone to wear and provide superior corrosion resistance.
Lubricated Plug Valve Applications
These valves are considered to be high-maintenance plug valves; they are commonly employed in special applications. For example, lubricated plug valves work effectively in operations that use fluids containing slightly abrasive particles, such as polluted upstream applications, gas pipeline systems requiring bypass valves, and blow-down valves on valve stations and kicker valves.
Some industries where Lubricated Plug valves are used:
- Pulp & Paper, Mining, for metal works.
- Wastewater management, Midstream transportation, Downstream processing, etc.
Does All Plug Valve Need Lubrication?
Not all plug valve use lubrication to work properly, there are other types of plug valves which do not require lubrication those are called non-lubricated plug valves. The main types of non-lubricated plug valves are:
- Lift-type plug valve.
- Elastomer sleeved plug valve.
- Fully lined plug valve.
This type of valve employs a non-metallic elastomeric sleeve or liner. This non-metallic sleeve reduces the friction between the plug and the valve body. Non-lubricating plug valves required less maintenance. Because of the non-metallic seat, these valves cannot be utilized in high-temperature applications.
Both lubricating and non-lubricating valves are capable of providing a bubble-tight cut-off and are small in size.
Summary
As discussed in this article, a Lubricated Plug Valve is a reliable and standard valve designed for general isolation purposes in a variety of liquid, gaseous and slurry services, including media containing slightly abrasive particles. If you’re reading this, we’d like to thank you and hope you find the information given helpful.
Please get in touch with us if you need any more information regarding the article. You can also leave a comment and express your viewpoint with us.
