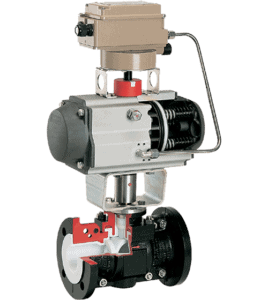
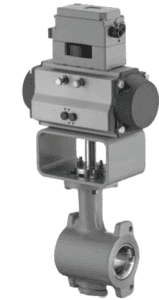
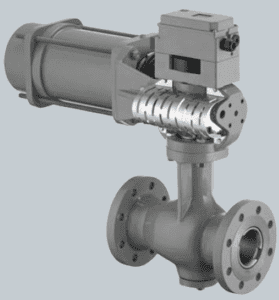
Rotary Plug Valve
Rotary Plug Valve
NTGD is professional rotary plug valve manufacturer, Don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any inquiry.
What is a rotary plug valve?
This is a valve designed with a plug component for regulating fluid flow. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design the valve such that the plug follows an eccentric path as it turns inside the valve. The plug in this valve does not make contact with the valve seat unless it rotates within a few degrees at the shutoff position. When the plug contacts the seat, the seating surfaces align to create a shutoff. Rotary plug valves are meant for handling liquids, gases, vapor, and slurries in demanding and general flow control applications. Rotary plug valve manufacturers also recommend this type of valve for use in applications that have high possibility of erosion and cavitation. These valves are widely used in different industries because of their ability to handle high fluid flow, compact size, shaft seal design, and superior rangeability. This valve is also able to handle high pressure and a wide range of temperatures between -100 oC to around 600 oC.
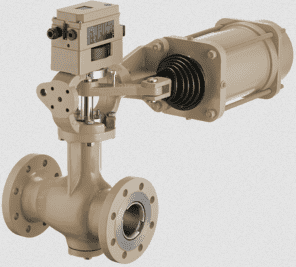
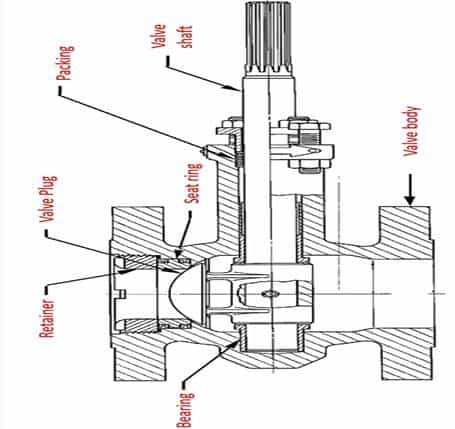
Components of a rotary plug valve
Actuator
The actuator is the component tasked with providing the power that starts, stops, or regulates fluid flow through the valve. The actuator has an output shaft mechanism that connects to the valve stem ensuring continuous power transmission when required to.
Shaft
The shaft is a component of the rotary plug valve that connects the valve plug to the actuator mechanism. Rotary plug valve manufacturers machine the shaft from high-strength metallic materials to ensure it has high strength enough to operate the valve plug even where high torque is involved.
Valve plug
This is the main component of a rotary plug valve which is tasked with starting and stopping fluid flow. The plug operates by making rotations about the valve shaft to either open or close fluid flow.
Seat
The seat is a component installed on the interior of the valve body. The seat is the component on which the valve plug rests when the valve is closed. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design this seat using different materials which could be metallic, plastics, thermoplastic, or rubber. Depending on the material used to make the seat, the valve can be used in some applications but not others. For example, for high temperatures, metallic seats are needed but not plastic seats.
Valve body
The body is a strong component that houses internal parts like the seat, seals, and valve plug. Rotary plug valve manufacturers make the valve body from strong materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and ductile iron among others. These high strength materials ensure that the valve body is strong enough to protect internal parts against impact damage. Also, the high strength ensures the valve can withstand high fluid pressure and high temperatures. The body contains the valve ports that enhance the connection between the valve and the pipe.
Crank mechanism
This mechanism is created by use of a camshaft component to create cam motion that helps to move the valve plug into the seat to provide fluid flow closure. Such a mechanism results in less torque on the valve plug when it breaks from the seat. As such, the rotary plug valve will not experience wear mostly seen in other valves whose plug or disc keeps constant contact with the valve seat.
Bearing
This component is mounted on the interior bottom of the valve body. It serves to support the valve shaft as it rotates to operate the valve plug.
Gasket
This is a component that helps to prevent fluid leakage between two connected components such as the valve body and the pipe.
Gland packing
This is a contact type of seal that is placed on the bonnet to prevent dirt entering in the valve body. It also helps to prevent fluid leakage through the valve shaft or bonnet.
How does a rotary plug valve work?
Rotary plug valves operate by rotating the valve shaft. The valve shaft is connected to the valve plug so that any rotation on the shaft causes the plug to rotate either to open or close fluid flow depending on the direction of rotation. The plug and shaft are eccentrically positioned to each other. This allows the valve plug to contact the valve seat only when it is in the closed position. Rotary plug valve manufacturers employ this eccentric valve design to help the plug clear the seat without initial torque when the valve shaft is rotated from the closed to open position. As such, the friction forces are reduced to minimum which makes rotary plug valves suitable for use in many applications for regulating fluid flow. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design this valve such that it can open smoothly as it provides stable fluid flow control at small opening angles. The fluid in this valve can flow in either direction of the valve.
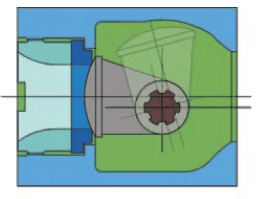
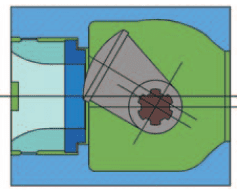
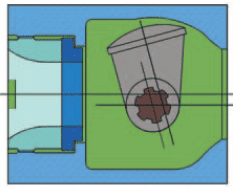
Types of rotary plug valves
PTFE-lined rotary plug valves
This is a rotary plug valve in which the interior part of the valve is covered using PTFE thermoplastic material. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design this valve for use in applications that involve corrosive fluids such as alkali and acids. PTFE material is also very strong and it has high melting point of around 250 oC. As such, this valve can be used in such critical conditions where the temperature and pressure are high. However, at temperatures above 250 oC, this valve cannot be used as the PTFE material will be melted down.
Figure: PTFE-lined rotary plug valve.
Pneumatic rotary plug valves
This is a rotary plug valve that operates by using a pneumatic actuator. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design an automated system that helps to determine when to open or close the valve. This type of valve employs a compressed gas to operate the valve. The actuator consists of gas chambers that help to compress the gas. The compressed gas acts on the actuator piston forcing it to create torque. This torque is used to operate the valve to either close or open fluid flow. Pneumatic rotary plug valves become very important when it comes to sanitary applications such as foods, beverage and pharmaceuticals among others. The use of this valve in such sanitary applications is enhanced by the fact that the gas used to operate the valve can be filtered to remove any dirt that may result in fluid contamination.
Figure: Pneumatic rotary plug valve.
Electric rotary plug valves
This is the rotary plug valve that is operated by use of an electric actuator. This valve is very versatile as it can be used in all industrial applications due to availability of electricity and its cleanliness. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design this valve with an electro-mechanical system that helps in converting electrical energy to mechanical energy. This mechanical energy in terms of torque is the one used to operate the valve to regulate fluid flow. Electric rotary plug valves can be used in different applications ranging from sanitary to wastewater applications. Compared to the pneumatic valve type, this valve has low operating costs and thus low maintenance costs. This valve is also very accurate in controlling the flow.
Figure: Electric rotary plug valve.
Hydraulic rotary plug valves
This is a rotary plug valve that operates by use of a hydraulic actuator. This valve is very powerful relative to other valves. The high torque output is enhanced by use of hydraulic fluid which is incompressible. This valve is suitable for use in such applications where a lot of torque is needed to open, regulate or close the fluid flow. However, this valve is limited for use in high-temperature applications as well as applications that need high levels of hygiene.
Applications of rotary plug valves
- Rotary plug valves are used in the oil refinery industries.
- This valve is used in the manufacturing of petrochemical products such as soap, plastics, and solvents among others.
- Rotary plug valves are used in chemical processing plants.
- They are used in the transportation of natural gas due to their fire-safe properties.
- These valves are used in steam power generating plants to control steam that powers turbines for electricity production.
- Rotary plug valves are used in the petroleum industry.
- These valves are used in mining industries due to their ability to control the flow of slurries and sludge without blockage.
- They are used in the manufacturing of paper and pulp.
- Rotary plug valves are used in water supply and wastewater treatment as they can withstand slurries.
- They are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
- They are used to control the flow of highly viscous fluids like coal tar and sulfur by incorporating heating jackets.
Advantages of rotary plug valves
- These valves are of high strength relative to other valves.
- Rotary plug valves are durable compared to other valves.
- They are resistant to corrosion from different chemicals.
- These valves are fast in operation.
- They are fire-safe making them suitable for use in gas and petroleum products.
- Rotary plug valves are free from fluid leakage due to the tight seals used.
- These valves are versatile as they have been used to control fluid flow in different industries.
- They can withstand high temperatures and high pressure.
- They can withstand slurries and sludge without blocking.
- Rotary plug valves have a high flow coefficient and high rangeability.
- These valves are bi-directional allowing fluid flow to the direction of choice.
- They are of simple and compact construction.
- They are easy to install and repair.
Disadvantages of rotary plug valves
- Rotary plug valves are more expensive compared to other valves.
- Most of these valves are heavy duty requiring large torque to operate and thus cannot be operated manually.
Troubleshooting rotary plug valves
Leakage through the valve-pipe connection
- Loose connection. Tighten the connecting bolts and nuts to attain the torque recommended by the rotary plug valve manufacturer.
- Worn out or damaged gasket. Replace the gasket.
- Excessive flow pressure. Reduce the working pressure. The valve should only be used at the pressure recommended by the rotary valve manufacturer.
Leakage through the seat
- Damaged seat. Replace the seat.
Leakage through the body-bonnet connection
- Loose connection. Tighten the bolts and nuts.
- Worn out or damaged packing. Replace the gland packing.
The actuator does not operate
- No power supply. Ensure power is supplied to the actuator.
- Low voltage. Ensure the voltage value is as recommended by the rotary plug valve manufacturer.
No fluid flow through the valve
- Pipe blockage. Check the pipe feeding the rotary plug valve for blockage and remove any blocking material.
- The valve is not open. Ensure the valve is open.
The valve needs a lot of torque to operate
- Blockage in the valve. Open the valve and remove any foreign materials causing blockage.
Summary
Rotary plug valves are valves that have the plug and the valve shaft eccentric. This type of valve is very reliable and of simple design which has made it more preferred in many industrial applications. This valve is easy to open as it needs less torque due to minimal friction between the valve seat and the plug. Rotary plug valve manufacturers design this valve such that the valve plug and the seat make contact only when the valve is being closed. This helps to reduce friction which not only makes valve operation smooth but also reduces wear on the valve seat and the valve plug.
Rotary plug valve manufacturers produce varieties of these valves among them PTFE-lined rotary plug valves, hydraulic rotary plug valves, pneumatic rotary plug valves, and electric rotary plug valves among others. Applications of these valves include petrochemicals, chemical processing, oil refinery, gas and petroleum, wastewater treatment, mining, paper and pulp manufacturing, and HVAC systems among others. Advantages of using this valve include bi-directional fluid flow, versatility, high coefficient flow, high rangeability, high strength, fast operation, and corrosion resistance.